Home > Power Platform > All you need to know about Power Platform Environments
Power Platform Environment
Power Platform Environment is like a container or workspace that holds your apps, flows (from Power Automate), connections, data (via Dataverse), and more.
🔑 Key Points:
Each environment is isolated—apps and data in one environment are separate from another.
You can create multiple environments for different purposes:
Development – where apps are built and tested
Test/UAT (User Acceptance Testing) – for user feedback
Production – live environment used by end users
🧠 Why Environment Matter:
Help organize apps by department, project, or lifecycle stage.
Allow for role-based access control.
Enable better data governance and security policies.
Support ALM (Application Lifecycle Management) best practices.
⚙️ Types of Environment:
Default Environment – automatically created for every user; ideal for personal or ad-hoc apps.
Sandbox Environments – created for development and testing apps, workflows etc.
Trail Environment – All features of Production Environment unlocked, works only for 30 days
Production Environment – created for production end user
Developer Environment – free, personal space created via the Power Apps Developer Plan.
Power Platform Environment Roles Explained
Environments in Power Platform come with two built-in roles that help manage access and control:
Environment Admin
Users with the Environment Admin role have full control over the environment. They can:
➕ Add or remove users or groups from Admin or Maker roles
🗃️ Provision a Dataverse database for the environment
👁️ View and manage all resources created within the environment
🛡️ Set Data Loss Prevention (DLP) policies to protect data
🔄 After setting up a Dataverse database, they can also act as a System Administrator
Environment Maker
Users with the Environment Maker role can create and use resources but cannot manage the environment itself. They can:
- 🧩 Build Canvas apps, Model-driven apps, and portals
- 🔗 Create connections, custom connectors, and flows using Power Automate
- 🚀 Experiment and innovate without needing admin privileges
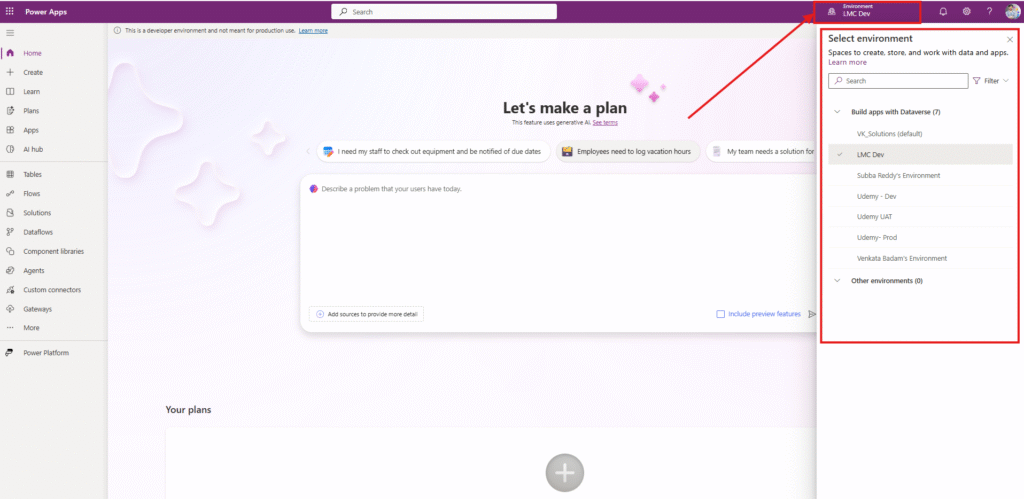
Important Links
- Official Microsoft Learn Power Platform Environment:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/power-platform/admin/environments-overview?tabs=new - What are Solutions in Power Platform? click here

[…] Environment and Solutions for ALM and Project management […]